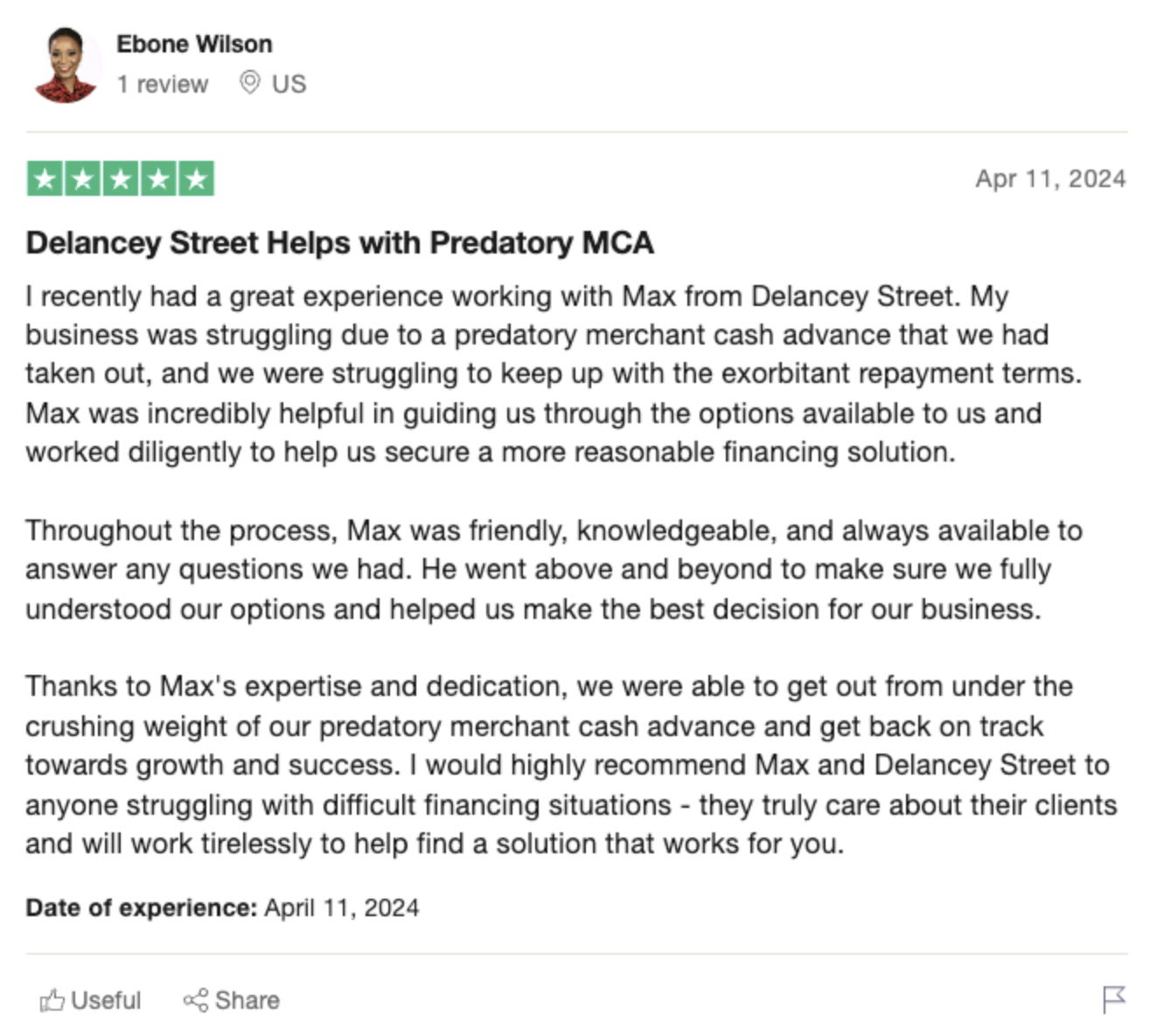
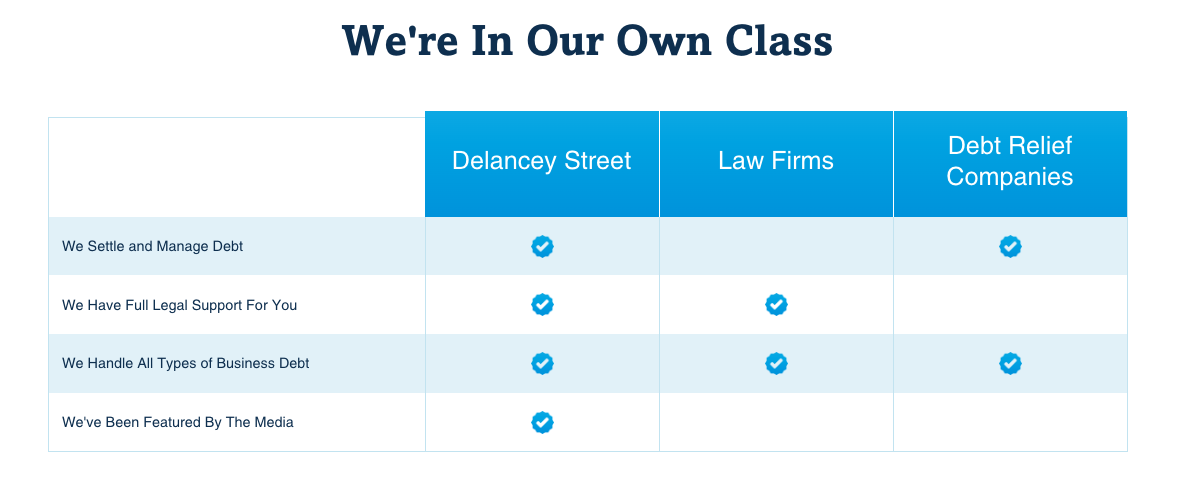
Introduction to Investment Portfolios
What is an Investment Portfolio?
An investment portfolio is a collection of assets. It includes stocks, bonds, real estate, and cash. You create it to achieve financial goals. It’s about balancing risk and reward. It’s not just for the wealthy. Anyone can build one. Start small. Grow over time. The key is diversification. Don’t put all your eggs in one basket. Spread your investments.
Why diversify? It minimizes risk. One asset might go down, another goes up. It balances out. It’s a strategy. Protects your investments. Think of it like a safety net. You need to understand the types of assets. Stocks offer growth. Bonds provide stability. Real estate gives tangible value. Cash ensures liquidity. Each plays a role. Know their benefits and risks.
 -
-Types of Assets in a Portfolio
- Stocks: Ownership in a company. High growth potential. High risk.
- Bonds: Loans to companies or governments. Lower risk. Steady income.
- Real Estate: Physical property. Long-term growth. Requires management.
- Cash: Liquid assets. Low risk. Low return.
Table: Types of Assets and Their Characteristics
| Asset Type | Risk Level | Return Potential | Liquidity |
|---|---|---|---|
| Stocks | High | High | High |
| Bonds | Low | Moderate | Moderate |
| Real Estate | Moderate | High | Low |
| Cash | Low | Low | Very High |
Investing is personal. Your goals and risk tolerance shape your portfolio. Be realistic. Understand your limits. Are you comfortable with high risk? Or do you prefer safety? This determines your asset mix. Regularly review and adjust. Markets change. Your situation changes. Stay flexible. Stay informed.
How to Build an Investment Portfolio
Start with your goals. What are you saving for? Retirement? A house? Education? Each goal has a timeline. Short-term goals need liquid assets. Long-term goals can handle more risk. Next, assess your risk tolerance. High risk can mean high reward, but also high loss. Low risk means steady but smaller returns.
Choose your assets. Diversify. Mix different types. Balance risk and reward. Allocate your assets. Decide how much in each category. Adjust over time. Rebalance your portfolio. Keep it aligned with your goals. Monitor performance. Track your investments. Make informed decisions. Adjust as needed.
 -
-Table: Steps to Building an Investment Portfolio
| Step | Action |
|---|---|
| Set Goals | Identify financial goals |
| Assess Risk Tolerance | Determine comfort with risk |
| Choose Assets | Select a mix of stocks, bonds, real estate, and cash |
| Allocate Assets | Decide how much to invest in each asset type |
| Monitor Performance | Regularly check the performance of investments |
| Rebalance Portfolio | Adjust asset allocation to stay aligned with goals |
Importance of Diversification
Diversification spreads risk. It balances your portfolio. If one investment fails, others can succeed. It’s like insurance. Protects against market volatility. Reduces impact of losses. Enhances potential for gains. Diversify across asset classes. Mix stocks, bonds, real estate, and cash. Diversify within asset classes. Different sectors, industries, and regions. Avoid over-concentration.
Rebalancing Your Portfolio
Rebalancing keeps your portfolio on track. Over time, asset values change. Your portfolio might shift. It may become unbalanced. Rebalancing means adjusting. Selling some assets, buying others. Realign with your goals. It’s about maintaining the right mix. Regular intervals work best. Quarterly, semi-annually, or annually. It’s a disciplined approach. Avoids emotional decisions.
Table: Rebalancing Strategies
| Strategy | Description |
|---|---|
| Periodic | Rebalance at regular intervals (e.g., quarterly) |
| Threshold-based | Rebalance when asset allocation deviates by a set percentage |
| Combined | Use both periodic and threshold-based strategies |
Managing Investment Risk
Risk is inherent in investing. Manage it effectively. Diversify your portfolio. Rebalance regularly. Stay informed about market trends. Understand each investment. Know the risks involved. Don’t chase high returns blindly. Balance risk and reward. Use a mix of asset classes. Consider your risk tolerance. Make informed decisions.
 -
-Benefits of Professional Help
Consider a financial advisor. They offer expertise. Help you set goals. Assess risk tolerance. Choose and manage investments. Provide ongoing advice. They understand market trends. Offer personalized strategies. Save you time and stress. They can help you stay disciplined. Avoid emotional decisions.
Table: Benefits of Financial Advisors
| Benefit | Description |
|---|---|
| Expertise | Knowledge of market trends and investments |
| Goal Setting | Assist in setting and achieving financial goals |
| Risk Assessment | Help determine and manage risk tolerance |
| Personalized Strategies | Tailored investment plans |
| Ongoing Advice | Continuous support and adjustments |
| Time-saving | Handle the complexities of investing |
Common Investment Mistakes to Avoid
Avoid these common mistakes. Don’t ignore diversification. Don’t chase past performance. Avoid high fees. Monitor your portfolio. Don’t time the market. Stay disciplined. Keep emotions in check. Regularly rebalance. Have a plan. Stick to it. Adjust as needed. Avoid speculative investments. Know your risk tolerance. Stay informed.
 -
-Investing requires discipline. It’s not about quick gains. It’s about long-term growth. Stay patient. Stay focused. Avoid impulsive decisions. Follow a strategy. Rebalance your portfolio. Seek professional help if needed. Stay informed.
Table: Common Investment Mistakes and Solutions
| Mistake | Solution |
|---|---|
| Lack of Diversification | Spread investments across asset classes |
| Chasing Past Performance | Focus on future potential |
| Ignoring Fees | Choose low-cost investment options |
| Market Timing | Stick to a long-term plan |
| Emotional Decisions | Make disciplined, informed choices |
Conclusion
Building an investment portfolio takes effort. It requires knowledge. Set clear goals. Assess your risk tolerance. Diversify your investments. Rebalance regularly. Manage risks. Consider professional help. Avoid common mistakes







